Vertical Farming: The Future of Food for Our Cities
As cities grow bigger and populations rise, one of the biggest challenges we face is how to feed everyone with fresh, safe, and sustainable food. Traditional farming is land-intensive, depends on monsoon rains, and often struggles with problems like pests, unpredictable weather, and soil degradation.
But there’s a modern solution that could revolutionize urban food production: Vertical Farming.
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is a modern method of growing plants in stacked layers inside a controlled environment, like in tall buildings or warehouses. Instead of soil, it uses hydroponics or aeroponics to grow crops.
- Hydroponics: Growing plants in nutrient-rich water.
- Aeroponics: Growing plants where roots are misted with water and nutrients.
This method allows year-round production, meaning fresh vegetables and fruits are always available—even in crowded cities like Mumbai, Delhi, or Bengaluru.
Think of a multi-story building where every floor is a farm—this is vertical farming!
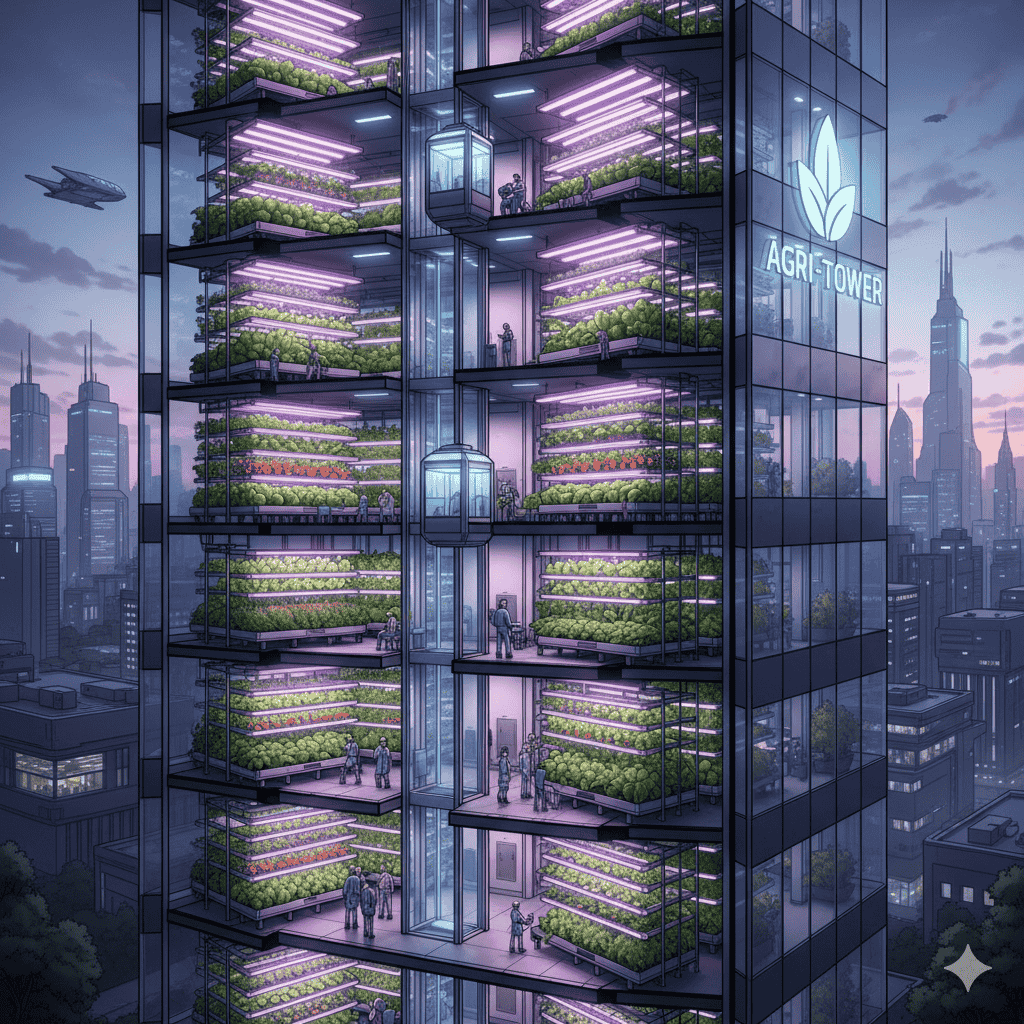 Vertical Farming: A Peek to the Future
Vertical Farming: A Peek to the Future
Why Vertical Farming is Important for Cities
As more people move to cities, urban sprawl causes major issues like:
- Lack of space for traditional farms.
- Rising food transport costs because food must travel hundreds of kilometers to reach city markets.
- Malnutrition among poor communities due to expensive or unavailable fresh produce.
Vertical farming can solve these problems by bringing farms into the heart of the city.
Benefits:
- Fresh and Healthy Food: No need for chemical pesticides; produce is clean and safe.
- Space Saving: Uses up to 90% less land compared to traditional farming.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics and aeroponics save up to 95% of water—perfect for water-scarce cities.
- Employment Opportunities: New jobs for urban youth in tech-driven agriculture.
- Year-Round Supply: No waiting for the right season; crops grow continuously in controlled environments.
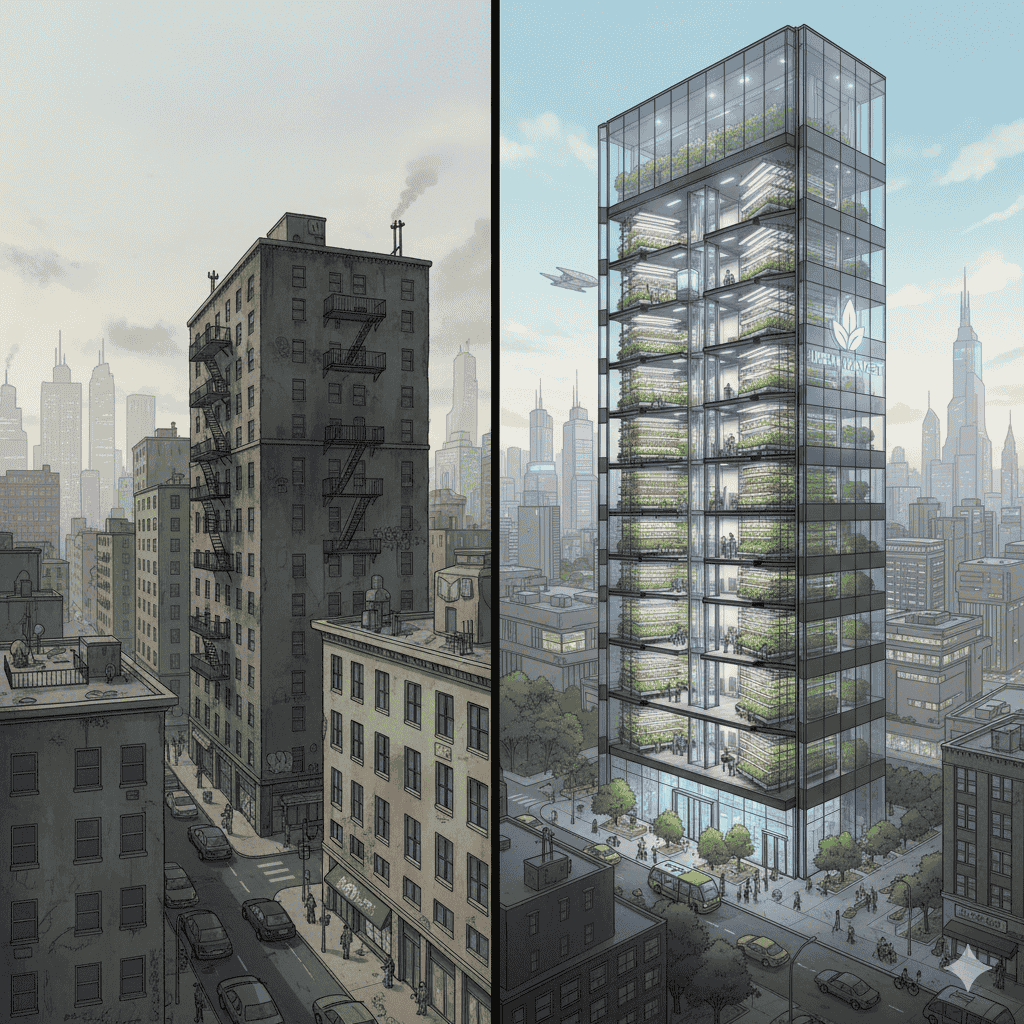 Diagrammatic Representation: Life with and without Vertical Farming
Diagrammatic Representation: Life with and without Vertical Farming
Challenges Slowing Down Vertical Farming
Even though vertical farming sounds amazing, it’s growing slowly because of certain challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Setting up controlled systems and LED grow lights is expensive.
- Lack of Specialized Equipment: There aren’t enough companies making hydroponic or aeroponic systems for tall buildings.
- Financial Barriers: Small farmers and startups don’t get enough government or private funding.
- Awareness: Many people still don’t know about this concept.
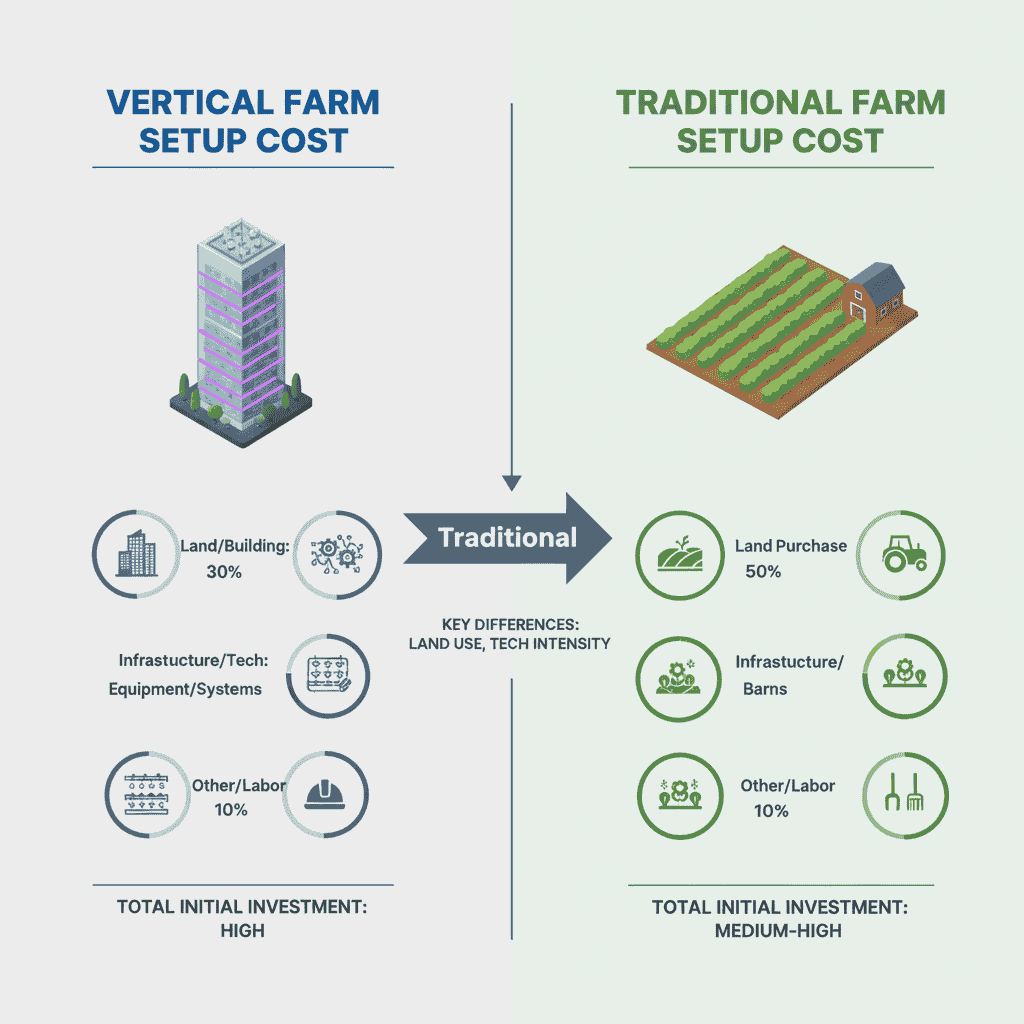 Key Differences between the Vertical Farm Setup & Traditional Farm Setup
Key Differences between the Vertical Farm Setup & Traditional Farm Setup
How Vertical Farming Can Change Urban India
Imagine a building in the middle of Mumbai that produces fresh spinach, strawberries, and lettuce—all grown locally, without needing to travel hundreds of kilometers. This could:
- Reduce transportation emissions,
- Lower vegetable prices, and
- Provide nutritious food to low-income families.
It can also reduce malnutrition, which is still a problem in many urban slums.
Vertical Farming and the Environment
Cities often damage natural ecosystems by replacing green spaces with concrete. Vertical farms can mimic natural ecosystems by supporting:
- Pollinator insects like bees,
- Water recycling systems, and
- Reduced use of harmful chemicals, keeping the urban environment balanced.
Future Outlook
For vertical farming to become common in Indian cities, we need:
- Government support and policies for sustainable urban agriculture.
- Affordable technology like efficient LED grow lights and low-cost hydroponic systems.
- Public awareness campaigns to educate people about local, sustainable food production.
With proper planning, vertical farming can transform urban food systems, making cities greener and healthier.
Conclusion
Vertical farming is not just about growing vegetables; it’s about growing a better future. By combining technology, sustainability, and smart planning, we can ensure everyone in our cities has access to fresh, nutritious food while protecting our environment.
Happy Farms → Healthy Cities → Stronger Nation
References
- Despommier, D. (2010). The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Urban Agriculture Reports, 2024.
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India (2023).
- Kalantari, F., et al. (2017). Opportunities and Challenges in Vertical Farming.
- ResearchGate. Controlled Environment Agriculture in Urban Areas.

